AWS LAMBDA COLD START
Introduction (What is Cold Start)
- When a serverless function is running, it stays in an active state only as long as it is in the running state.
- Containers also remain in an active state only during this duration of time.
- After some time these containers become inactive if no activity is there.
- Functions will go in an inactive state if no execution is there.
- Inactivation of our functions or containers is done by the cloud provider that we are using say for example – AWS or GCP.
- When we invoke an inactive serverless function that start is called a Cold Start.
- Delay occurs because the function or the container is in an inactive state, and it takes some time for the cloud provider to restore their state.
- Spinning up a new container after it has been in an inactive state causes the delay.
- This is how cold start affects the execution time of a serverless function.
- In short, we can say that cold start results in a longer execution time of the serverless functions resulting in the overall delay of the application.
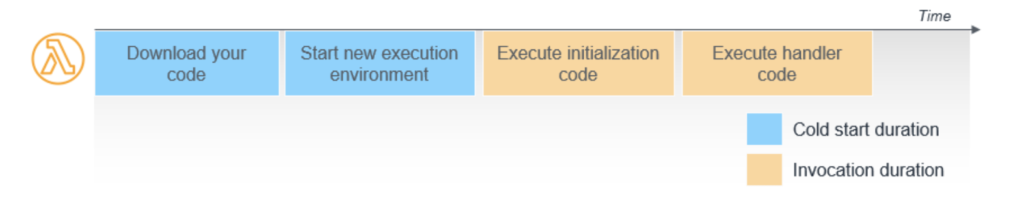
- In the above diagram, the first two steps are the cold start duration.
- Firstly, the download of our code happens then a new environment is set up.
- Although we are not charged for this time duration it causes a delay in the execution of our function.
- Once the execution is completed, the execution environment is frozen for a certain period of time.
- If another request arrives for the same function, the service may reuse the environment that is frozen to avoid latency and for better performance.
- This use of the previous environment is called a warm start as it doesn’t download your code and set up the environment again.
- According to research cold start invokes only under 1% of the invocations.
- The duration of cold start varies from 100ms to up to 1 sec.
Reasons for the Cold Start
- Whenever the function is updated or changed there will always be a cold start as it reloads the code and creates a new environment.
- When the function is not invoked frequently.
- If the programming language in which lambda is used has a higher latency or more dependencies.
Reducing Cold Start
- Provisioned Concurrency can be used if we need a predictable function start time.
- It means to increase the amount of concurrency during high demand and decrease it at the time of low demand.
- It can be done through AWS CLI and no need to make any changes to your code.
- Deciding the right memory size can also be helpful in reducing the cold start.
- Monitoring the performance of the lambda and setting up the configuration according to that only will also help.
- Caching can be used if the invocation is not very frequent or the data is not getting updated very frequently.
- Low Latency languages can be used to avoid delay while the execution.
Conclusion
- Cold Start is something that will take place.
- We need to understand our needs and define our configuration according to that.
- Provisioned Concurrency is one of the best ways to optimize the cold start.
- Better memory management is also very helpful.
References
- https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/operating-lambda-performance-optimization-part-1/
Still Curious? Visit my website to know more!
For more interesting Blogs Visit- Utkarsh Shukla Author
0 Comments
Add Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.







