More Than What Meets the Eye: A Deep Dive into Design
Imagine a beautiful car that doesn’t drive smoothly or an engine that runs perfectly but has a decaying, out-of-shape body. Would you still want to sit in it?

How do you perceive design?
Do you judge a book by its cover and believe that if it glitters, it’s gold?
Or do you prefer to delve deeper, looking beyond appearance and evaluating its functionality as well?
For a long time, the debate over the definition of design has been ongoing, with the explanation that “design is extremely perceptual.” While this explanation still holds true at a surface level, what about its functional aspect? After all, what truly matters is if the product, service, or experience fulfills its intended purpose for you.
In today’s world, it’s more important than ever to consider both the functional appeal and appearance of a design. Functionality is just a part of the overall user experience that people are willing to pay for. Let’s clarify this further by understanding design at its core definition.
What is Design?

Design is the process of creating and developing a plan or solution to a problem with the aim of improving functionality, appearance, and user experience.
Therefore, it’s safe to say that:
Good Design = Functionality + UI + UX
In this digital age, as more products and services move online, every component of good design is critical.
When these components are combined, they result in:
• Building trust and loyalty with users
• Increased engagement and usage
• Ultimately, the success of the product or service
Guardrails for Designers

If you’re a designer or aspire to be one, what are the crucial factors you should focus on before presenting your creation to the world? How do you create designs that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also usable, accessible, functional, and deliver a positive user experience? Here are the guardrails:
1. Usability: A design should be easy to use and have an intuitive UI that allows users to complete tasks quickly and efficiently.
2. Accessibility: The design should be inclusive, allowing people with disabilities to use and benefit from the product or service.
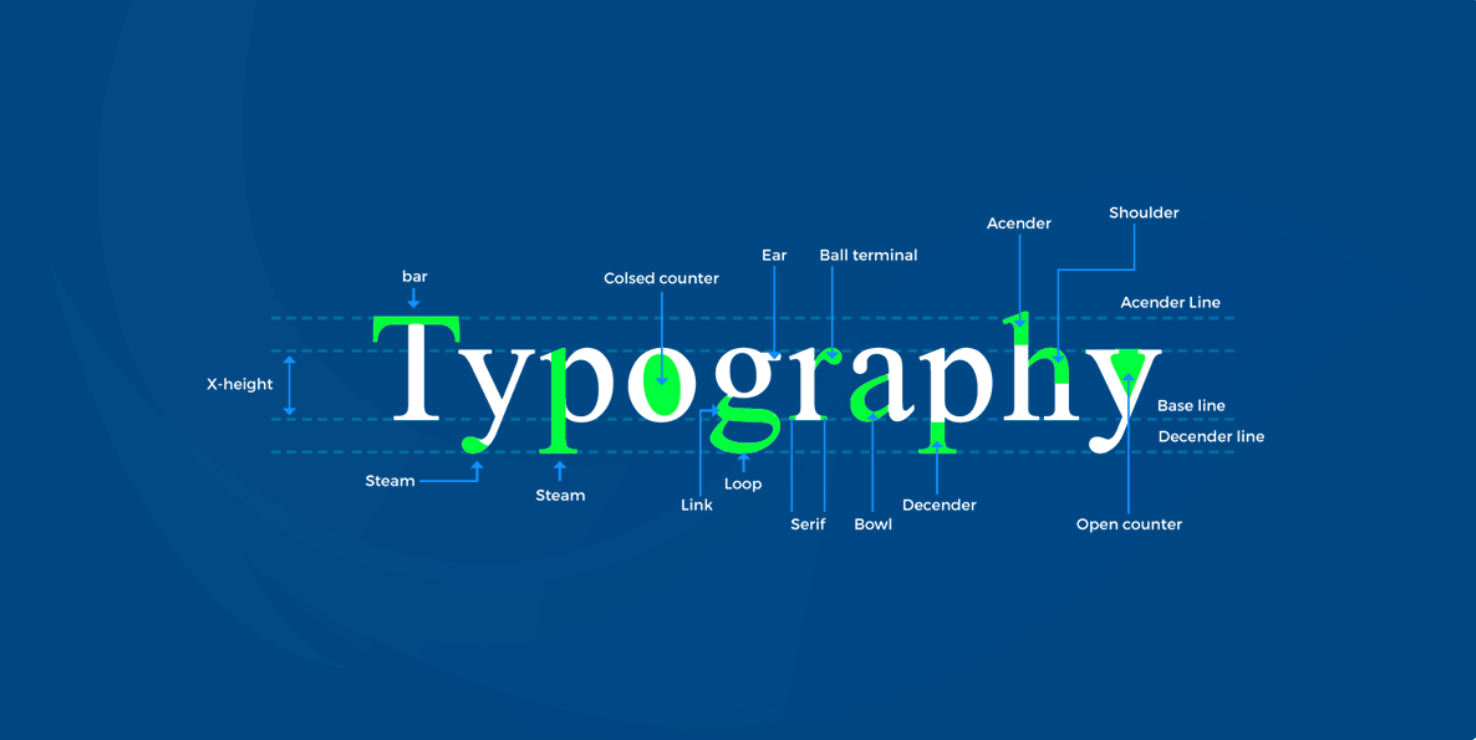
3. Aesthetics: The visual appearance of the design should be pleasing, with a balanced use of color, typography, and imagery that creates a cohesive look and feel.
4. Functionality: The design should serve its purpose and function well, whether it’s to interact, inform, or perform a task.
5. Human/User-Centered: The design should be centered around the user, taking into account their goals, behaviors, and feedback.
6. Innovation: Good design should challenge conventions and push boundaries, incorporating new technologies and approaches to create innovative solutions.
7. Context: The design should consider the context in which it will be used, including the physical and cultural environment and the needs and behaviors of the intended users.
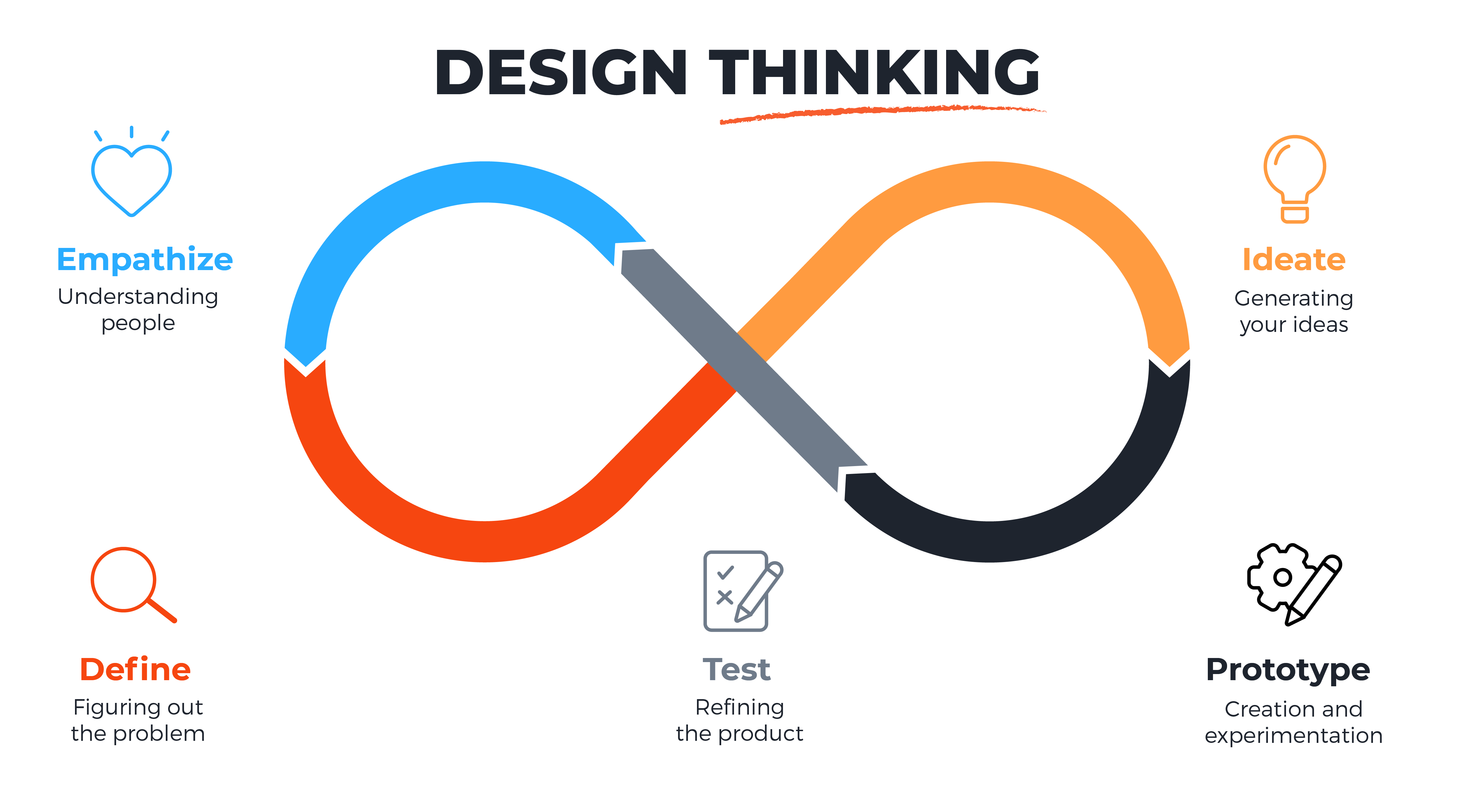
Design Thinking Process

The process of problem-solving with empathy, experimentation, and iteration always yields results. Here’s how it works:
1. Empathize: Designers aim to understand the user and their needs and desires by observing them, conducting interviews, and gathering data through other means.
2. Define: Synthesize the information gathered in the empathy stage to develop a clear problem statement that defines the problem.
3. Ideate: Generate a wide range of potential solutions to the problem, using brainstorming and other techniques to generate as many ideas as possible
4. Prototype: In this stage, create mockups of the ideas, using low-fidelity wireframes, or high-fidelity wireframes depending on the type of product or solution being developed.
5. Test: In this stage, test the prototypes with users and gather feedback and use the insights to refine and improve the designs.
What does the future hold?

The future of design will be shaped by advances in technology, changes in consumer behavior, and the evolution of design thinking.
Some of the key trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of design include:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML will increasingly be used to automate repetitive tasks and generate design concepts, freeing up designers to focus on more creative and strategic work.
2. Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR and AR): Immersive experiences will become more widely adopted and will play a greater role in product development and user experience design.
3. Personalization: The trend towards personalized experiences will continue, with designers increasingly using data and AI to create individualized products and services that meet the unique needs and preferences of each user.
4. Sustainability: As consumers become more aware of the impact of design on the environment, sustainable design practices will become increasingly important, and designers will focus on creating products and services that have a minimal impact on the environment.
5. Collaborative Design: Designers will increasingly work in multidisciplinary teams and collaborate with other stakeholders, such as developers, marketers, and product managers, to create more holistic and integrated products and services.
6. Human-Centered Design: Design thinking will continue to evolve and be embraced by more organizations, resulting in a greater emphasis on empathy, experimentation, and iteration in the design process.
7. Interdisciplinary Design: The boundaries between design disciplines will continue to blur, with designers increasingly working across traditional design specializations, such as graphic design, product design, and UX design, to create more integrated and holistic designs.
The future of design is exciting and full of potential, and designers will continue to play a critical role in shaping the products and services that impact our lives in new and meaningful ways.
Add Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.




Snigdha Samal
Indeed the future of UX is full of potentials. AI is going to infuse omnipotency into the applications and on the other, complex product requirements would push designers to design for an immersive or almost real world experience.
Great insightful article!