Data Modelling: The Art of Turning Data into Decisions
Introduction:
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are faced with a growing challenge: how to make sense of the vast amounts of data they collect. With so much information at their disposal, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. That’s where data modelling comes in – the art of turning raw data into meaningful insights that drive decision-making.
Data Modelling:
Data modelling is the process of organizing and analyzing data to extract maximum value from it. By creating a blueprint for how data should be structured and analyzed, data modellers help organizations make sense of their data and turn it into actionable insights.
At its core, data modelling is about understanding the following problems:
- What problems are you trying to solve?
- What insights do you hope to gain from your data?
- What questions are you trying to answer?
Once you have a clear understanding of your goals, you can start selecting the right data sources and choosing the appropriate data structures to support your analysis. This could include entities, attributes, and relationships, which represent the relationships between different data elements.
Data is changing the way the world functions. It can be a study about disease cures, a company’s revenue strategy, efficient building construction, or those targeted ads on your social media page; it is all due to data.
This data refers to information that is machine-readable as opposed to human readable.
For example, customer data is meaningless to a product team if they do not point to specific product purchases. Similarly, a marketing team will have no use of that same data if the IDs didn’t relate to specific price points during buying.
Note:
Data Modeling is the process of creating data models by which data associations and constraints are described and eventually coded to reuse. It conceptually represents data with diagrams, symbols, or text to visualize the interrelation.
Data Modeling thus helps to increase consistency in naming, rules, semantics, and security.
Types of Data Modeling:
There are three main types of data models that organizations use. These are produced during the course of planning a project in analytics. They range from abstract to discrete specifications, involve contributions from a distinct subset of stakeholders, and serve different purposes.
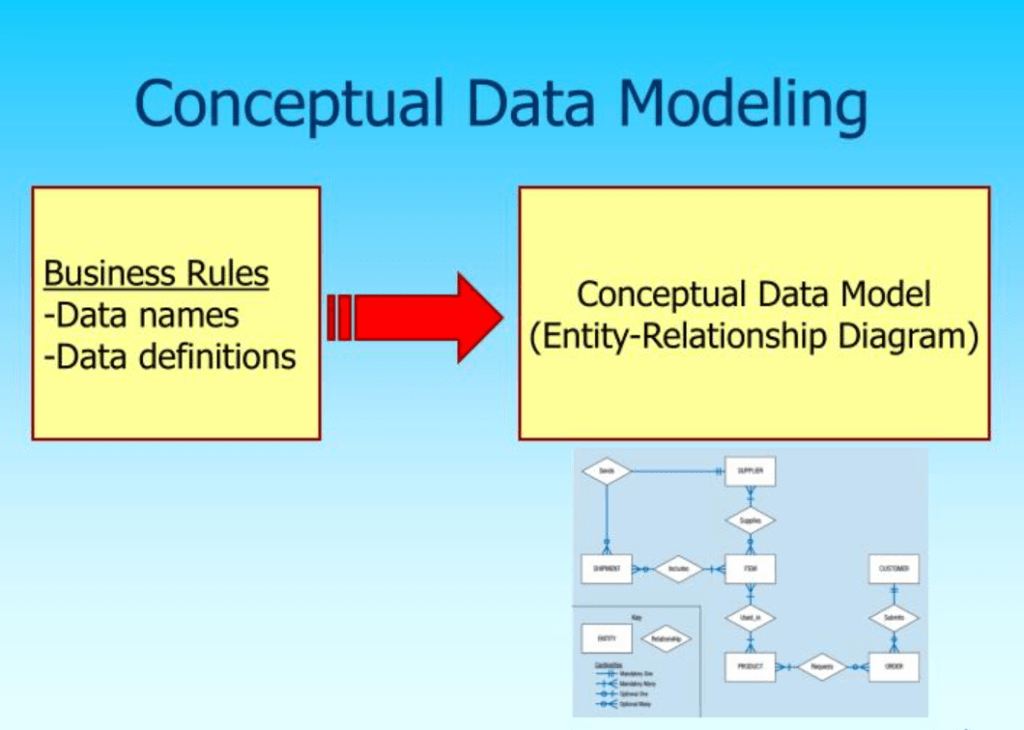
Conceptual Model:
It is a visual representation of database concepts and the relationships between them identifying the high-level user view of data. Rather than the details of the database itself, it focuses on establishing entities, characteristics of an entity, and relationships between them.
Logical Model:
This model further defines the structure of the data entities and their relationships. Usually, a logical data model is used for a specific project since the purpose is to develop a technical map of rules and data structures.
Physical Model:
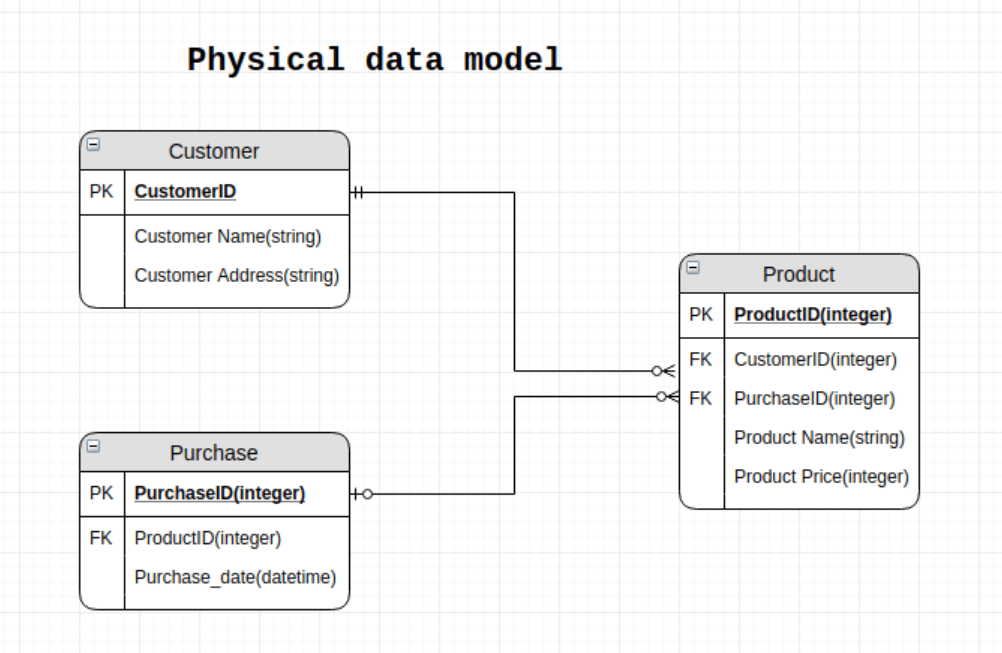
This is a schema or framework defining how data is physically stored in a database. It is used for database-specific modeling where the columns include exact types and attributes. A physical model designs the internal schema. The purpose is the actual implementation of the database.
Physical data modeling is the process of creating a detailed database design, including the specific design of tables, indexes, constraints, and other database objects. The physical data model represents the actual physical design of the database, including the storage and retrieval methods for data.
- In a physical data model, entities and relationships are represented as tables and columns, respectively. The physical data model also defines the data types for each column, such as integer, text, date, etc. In addition, the physical data model defines the relationships between tables, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships, using keys and constraints.
- Other physical data modeling techniques include the design of indexes, which improve the speed of data retrieval, and the design of constraints, which enforce the rules and relationships between data entities. The physical data model also includes the design of security features, such as user authentication and authorization, to ensure that data is secure.
Importance of data modelling:
Data modeling is a critical aspect of data management, and there are several reasons why it is important
- Improved data organization: Data modeling helps to organize data in a structured manner, making it easier to manage and maintain. It also ensures that data is stored in a consistent and standardized format, reducing the risk of data redundancy and inconsistencies.
- Better understanding of data: By visually representing data, processes, and their relationships, data modeling provides a clearer understanding of the data and how it is used within an organization. This can lead to improved decision-making and a more effective use of data resources.
- Improved data quality: Data modeling helps to identify and address any data quality issues early in the development process, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies in the data.
- Better database design: Data modeling helps to ensure that a database is designed to meet the specific needs of an organization. It takes into account the type of data that needs to be stored, the relationships between data entities, and the performance and scalability requirements of the database.
- Efficient database development: Data modeling helps to streamline the database development process, reducing the time and effort required to build a database. By using a data model as a blueprint, database developers can focus on implementing the database rather than figuring out how the data should be organized.
- Improved data analysis: Data modeling makes it easier to analyze data by clearly defining the relationships between data entities. This makes it easier to aggregate and manipulate data to support business decisions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, data modeling is a critical aspect of data management and plays a key role in ensuring the success of data management projects. By improving data organization, quality, and analysis, data modeling supports effective decision-making and the efficient use of data resources. Whether you are designing a new database or improving an existing one, data modeling is an essential step that should not be overlooked.
Add Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.