ElasticSearch – Using Python
Introduction
- ElasticSearch is a search engine platform that is used to store data and perform various analyses.
- It is based on the Apache Lucene Library.
- It stores the data in the document form, which is a non-relational form, basically a complex data structure.
- It is a distributed storage platform, that is having distributed clusters across the globe so that it can robust and easily accessible.
- Indexing is done to optimize the data storage and analyses capabilities.
- It is developed in JAVA, and is supported in many languages like JAVA, .NET, PYTHON, RUBY, C#, etc.
- It is the most popular search engine database.
Schema-Less
- Elasticsearch also has the ability to be schema-less.
- Documents can be indexed without explicitly specifying how to handle each of the different fields that might occur in a document.
- When dynamic mapping is enabled, Elasticsearch automatically detects and adds new fields to the index.
- This default behavior makes it easy to index and explore your data.
- Just start indexing documents and Elasticsearch will detect and map booleans, floating-point, and integer values, dates, and strings to the appropriate Elasticsearch data types.
- Ultimately, however, you know more about your data and how you want to use it than Elasticsearch can.
- You can define rules to control dynamic mapping and explicitly define mappings to take full control of how fields are stored and indexed.
Define Your Own Mapping
- Distinguish between full-text string fields and exact value string fields.
- Perform language-specific text analysis
- Optimize fields for partial matching
- Use custom date formats
- Use data types such as geo_point and geo_shape that cannot be automatically detected
- It’s often useful to index the same field in different ways for different purposes. For example, you might want to index a string field as both a text field for full-text search and as a keyword field for sorting or aggregating your data. Or, you might choose to use more than one language analyzer to process the contents of a string field that contains user input.
REST API’s
- Elasticsearch provides a simple, coherent REST API for managing your cluster and indexing and searching your data.
- For testing purposes, you can easily submit requests directly from the command line or through the Developer Console in Kibana.
- From your applications, you can use the Elasticsearch client for your language of choice: Java, JavaScript, Go, .NET, PHP, Perl, Python, or Ruby.
Searching Your DataEdit
- The Elasticsearch REST APIs support structured queries, full-text queries, and complex queries that combine the two.
- Structured queries are similar to the types of queries you can construct in SQL.
- For example, you could search the gender and age fields in your employee index and sort the matches by the hire_date field.
- Full-text queries find all documents that match the query string and return them sorted by relevance—how good a match they are for your search terms.
- In addition to searching for individual terms, you can perform phrase searches, similarity searches, and prefix searches, and get autocomplete suggestions.
Geo-Spatial Data
- Elasticsearch indexes non-textual data in optimized data structures that support high-performance geo and numerical queries.
Coding – Demonstration
- Install ElasticSearch on your system and start your ElasticSearch Engine. (https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/install-elasticsearch.html)
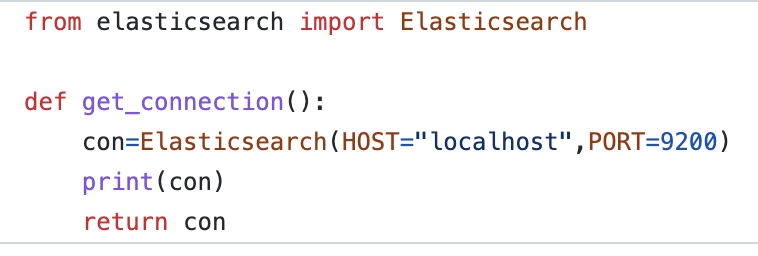
- Make a connection with ElasticSearch, and say it’s in your utils file.

- Create an index for your dataset.
- Code For checking, deleting and fetching all the indexes.

- Code for fetching, inserting, and querying dataset.

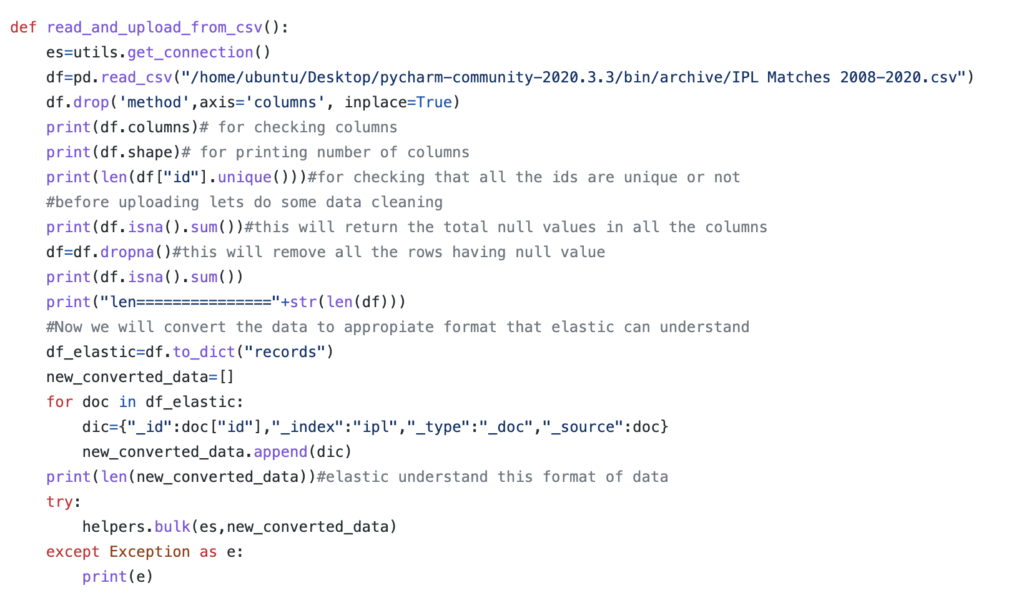
- Code to read data from CSV.
References-
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/search-analyze.html
- https://github.com/Utkarsh731/elasticSearch
- https://www.elastic.co/
Still Curious? Visit my website to know more!
For more interesting Blogs Visit- Utkarsh Shukla Author
0 Comments
Add Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.