How to Determine Forecastability of Demand?
In demand forecasting, there are a lot of cases where data scientists struggle to reach a good forecast error. On these occasions, they find it difficult to provide clear explanation to why some threshold of error is un-attainable no matter what technique is used. Forecast error of a product / event highly depends on its forecastability. If some event is unforecastable, it doesn’t even make sense to create a forecast model for it. We can rely on two parameters in order to determine whether the event is forecastable or not:
- ADI (Average Demand Interval) – Represents the measure of intermittency.
ADI = Total Number of Period / Number of non-zero demand occasions- CV2 (Squared Coefficient of Variation) – Represents the measure of variation excluding zero demand events.
CV2 = Standard Deviation of Population / Average of Population Based on these two parameters, we can classify the demand profile into one of these 4 different classes:
Smooth Demand
Erratic Demand
Intermitted Demand
Lumpy Demand
Smooth Demand
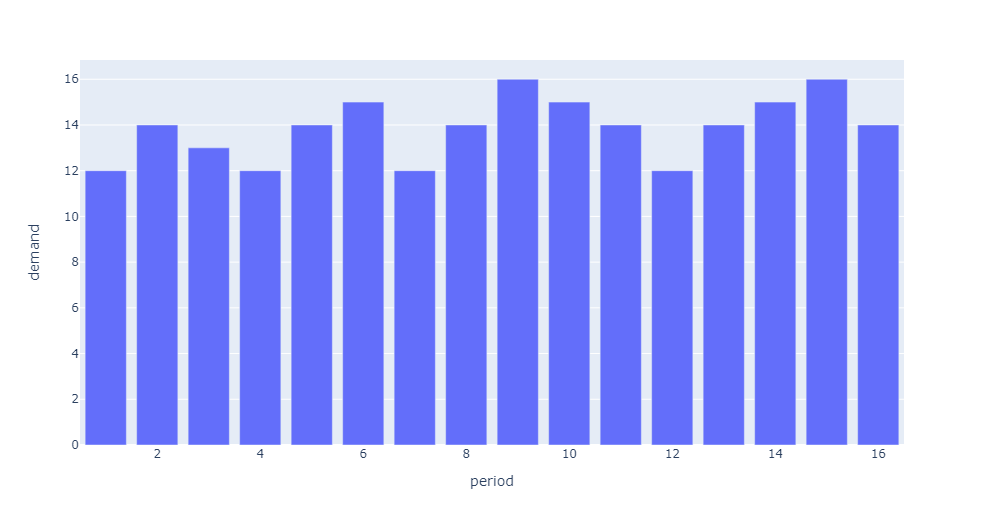
ADI < 1.32 & CV2 < 0.49 is classified as Smooth Demand because the demand is very regular in magnitude and occurrence. This class is very easy to forecast and low forecast error is attainable.
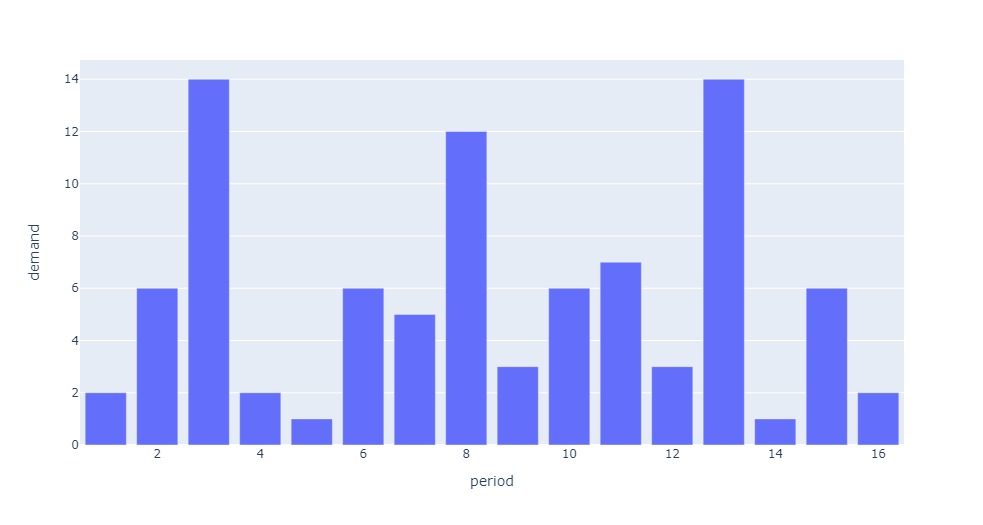
Erratic Demand
ADI < 1.32 & CV² >= 0.49 is classified as Erratic Demand because the demand is irregular in magnitude even-though it is in regular occurrence. Low forecast error will be hard to attain.
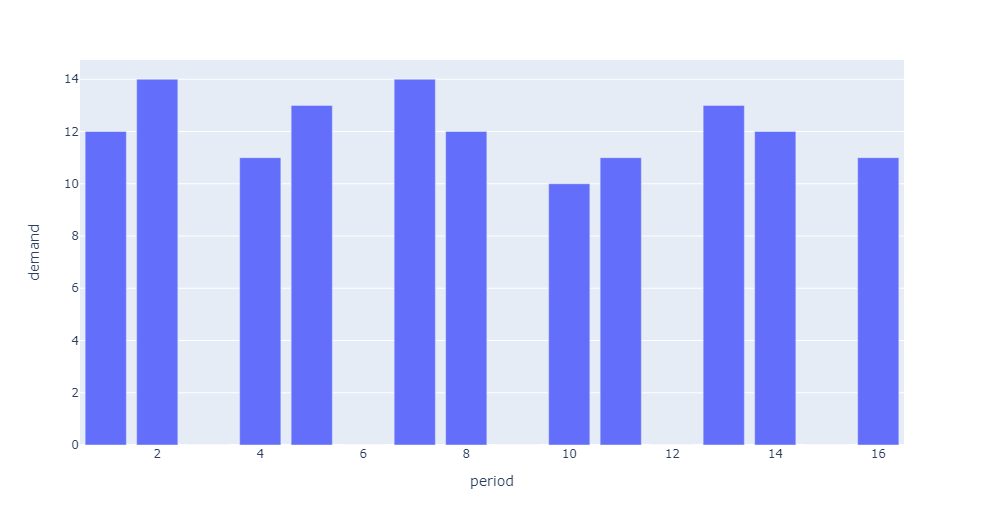
Intermittent Demand
ADI >= 1.32 & CV² < 0.49 is classified as Intermittent Demand because the demand is very regular in magnitude but it is very irregular in occurrence. Low forecast error will be hard to attain.
Lumpy Demand
ADI >= 1.32 & CV² >= 0.49 is classified as Lumpy demand because the demand is very irregular in magnitude and occurrence. It is improbable to create a forecast model that can have some predictability. Lumpy demand is unforecastable.
Determining the classification of historical demand makes it easy to plan out the research and development of a demand forecast model. This includes but no restricted to:
- Prioritization
- Algorithm selection
- Setting baseline for acceptable forecast error
Reference : https://www.ias.ac.in/article/fulltext/sadh/045/0051
Add Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.