Scaling Big Data: Best Practices for Managing Large Datasets
What is Big Data ?
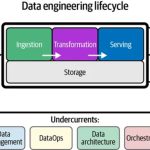
Big Data refers to the vast amount of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information that organizations generate daily. Consequently, this data becomes too large and complex for traditional databases to store or process efficiently. While structured data is neatly organized, semi-structured data, on the other hand, has some organizational elements but does not fit into relational databases. Moreover, organizations produce unstructured data, such as multimedia files, emails, and social media content, which lacks a predefined structure. Therefore, managing this data requires advanced tools to unlock its potential for analysis and decision-making.
Structured Data
Structured data organizes information in a predefined format, such as rows and columns, making it easy to store and analyze. A typical example of structured data can be found in relational database management systems (RDBMS), where data is neatly arranged for querying and processing.
Unstructured Data
On the other hand, unstructured data lacks a fixed format or organization, making it more challenging to process and analyze. Examples of unstructured data include multimedia files, emails, audio recordings, and images. Despite these challenges, unstructured data holds immense value, as approximately 85% of business data falls into this category, providing significant insights when appropriately utilized.
Semi-Structured Data
In contrast, semi-structured data sits between structured and unstructured data. It does not reside in traditional databases but contains some organizational properties that make it easier to process and interpret. Examples of semi-structured data include XML files and NoSQL databases, which offer flexibility while still maintaining a degree of structure for effective use.
4V’s of Big Data
The 4 V’s of Big Data represent the core characteristics that define and differentiate it.
![]()
Volume refers to the sheer scale of data generated daily, as businesses and systems produce massive amounts of information from various sources.
Velocity highlights the speed at which data is generated and analyzed, particularly in the case of streaming data that needs real-time processing for timely insights.
Variety emphasizes the diverse forms of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured formats such as text, images, videos, and more.
Lastly, Veracity addresses the uncertainty and reliability of data, focusing on ensuring its accuracy and trustworthiness to derive meaningful insights.
Together, these 4 V’s encapsulate the challenges and opportunities of Big Data in modern analytics.
How Big Data is useful ?
- To market relevant products
- New product development
- Cost Reduction
- Time Reduction
- Decision Making
- Scientific Research
Who uses Big Data ?
- Businesses
- Government
- Banks
- Healthcare
- Educational Institutions
Big Data is not just about handling massive volumes of information; it’s about unlocking actionable insights, driving innovation, and enabling smarter decision-making. Embracing Big Data with the right tools and strategies will empower organizations to stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world.