Introduction to the U.S. Health Care System | Inside a Business
When we talk about which country provides the best healthcare then we heard the names of countries like Canada, Sweden, Japan, Germany, Switzerland, or Singapore in the top list. As the quality of healthcare at any place depends on the below points:

- How much a country spends on it?
- What is the quality?
- How easily accessible healthcare is?
- What is the upfront cost of the same?
But, the above of these factors are not valid in the USA as medical bills are something that causes huge problems in the country. According to a report, before 2009 medical bills were a leading source of bankruptcy in America.
Thus to understand how US Healthcare works and how the giant insurance business came into the picture here, let’s take a dig and understand with a few terminologies.
Basic Definitions:

- Insured: The person whose name is on the policy and the person who will be compensated in the event.
- Plan Sponsor: Usually an employer if a business Provides health care insurance for its employees. If an individual is directly purchasing health insurance, then the individual is the plan sponsor.
- Insurer: The insurance company or the organization that underwrites the payments of losses or costs incurred by the policyholder.
- Provider: Although it may seem that a provider is a physician, a provider can also be a facility, such as a hospital or nursing home.
- Premium: The payment for the policy or insurance, even if you don’t make a claim.
- Benefits: The amount the insurer pays when a claim is filed.
- Policy: A contractual agreement between the insurance company and the insured that outlines the benefits, exclusions, and limitations of the coverage.
Insurance Plan Definitions:
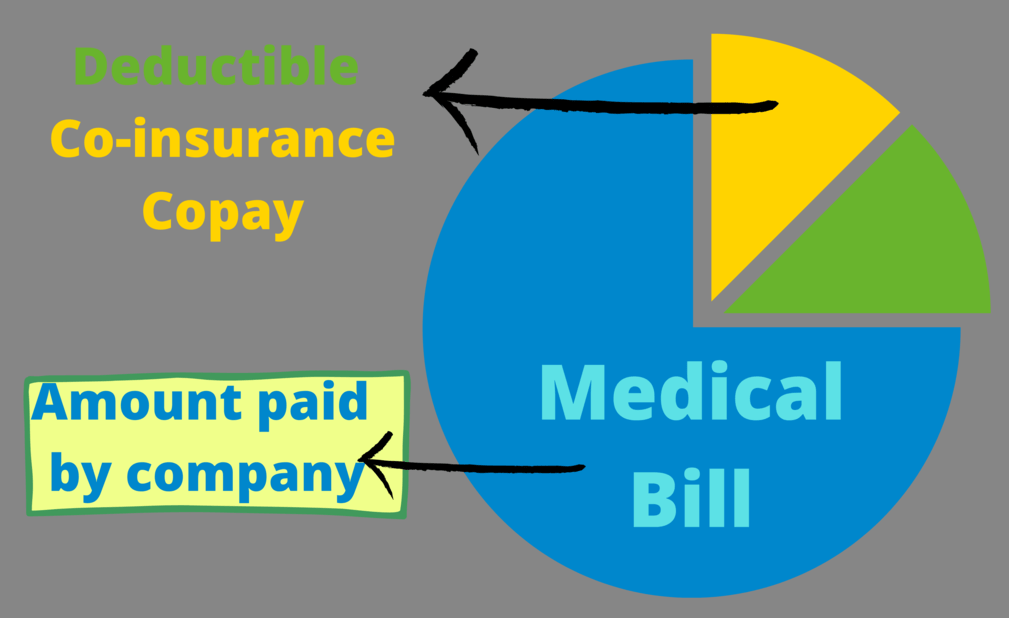
Deductibles: It is what you pay for your treatment even before your insurance company starts paying for it. This could be the minimum amount the insured must pay out of pocket which can be even $10,000 (depending on the plan bought). This is one time insurers have to spend for annual, quarterly, or monthly plans before taking the claim.
Coinsurance: This is the percentage amount every insurer has to share with the insurance company while paying for the medical bills. For example, if the co-insurance is 5% then the insured person must pay $2.5 from his pocket if the medical bill is $50.
Copayment: This is the fixed amount of money (not percentage like coinsurance) that the insurance buyer pays every time he/she visits the hospital. The payer is only liable to pay after the payment of Copay.
Out Of Pocket: Once the Sum insured amount of the tenure is fully paid by the payer (for one or multiple medical bills), other bills within the same tenure will be paid by the insurer himself, which is known as out of pocket.
Government-Sponsored Insurance
Now let’s move our focus briefly to how the government provides insurance through the Medicare, Medicaid, and TRICARE programs. Government-sponsored insurance is a huge business and it is growing due to the ACA (Affordable Care Act). Government insurance is also highly regulated, which makes it complex to administer.
CENTERS FOR MEDICARE & MEDICAID SERVICES
Government-sponsored insurance programs are run by CMS or the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. The CMS runs the Medicare program and also monitors the Medicaid programs that are offered by different states.
MEDICAID
Medicaid provides health care coverage to low-income families and individuals.
MEDICARE
The Medicare program provides health care coverage to the elderly. There are two trust funds that pay for Medicare. These funds are held by the U.S. Treasury and can only be used for Medicare. In 2011, Medicare service was reached almost 49 million people.
TRICARE
The TRICARE program provides health care coverage to military personnel and their families.
Non-Government Insurances – Commercial Insurance
This is the most profit-making insurance service that different insurance-providing firms offer. Commercial insurance can also be said to be private insurance. In the commercial market, most of the plans are group plans bought by employers for their employees. This is the most suitable option for the working population in the United States which covers their surged medical expenses. An insurance plan can be bought personally, but it is generally preferred to buy through group plan using some professional organization. There are two types of structures:
- Preferred Provider Organization (Patient can go out of network providers or hospitals)
- Health Maintenance Organization (Patient can only claim within the network provider/hospital services)
Thus, we have covered most of the necessary topics while talking about the US Healthcare industry and related business. According to a report of NAIC, the total earning from the American healthcare industry in 2020 was $31 Billion. Since this business is growing thus expect to give multi-fold revenue in the coming 5 years.
Hope all the readers like this article. We would like to hear from you via comments, so do share your valuable feedback or suggestions.
Add Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.







Utkarsh Shukla
Very well explained…