Generative AI For Digital Art and Design
Generative AI has revolutionized the field of digital art and design, enabling artists and designers to explore new creative frontiers. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning, generative models have opened up exciting avenues for creating captivating and unique digital artworks. In this blog, we will delve into the world of generative AI and its applications in digital art, discussing its potential, challenges, and future directions.

Generative AI Techniques in Digital Art and Design
One of the prominent applications of generative AI in digital art is the use of GANs. GANs consist of two neural networks: a generator network that creates new content, and a discriminator network that tries to distinguish between real and generated content. This adversarial relationship pushes the generator to create increasingly realistic and high-quality output.
Generative AI has been employed in various ways within digital art and design. Artists have utilized generative models for image synthesis and style transfer, allowing them to create visually stunning and unique artworks. Text-to-image generation has also been explored, where generative models transform textual descriptions into corresponding visual representations. Additionally, generative AI techniques have been used to convert sketches into realistic images and generate 3D models and animations, expanding the possibilities of digital art creation.
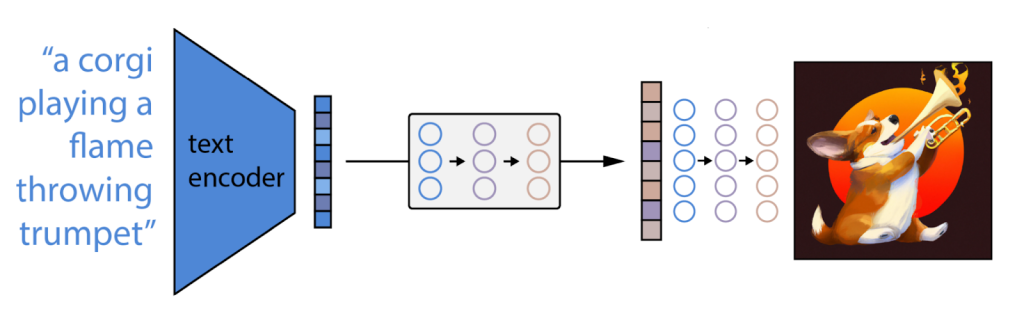
Case Studies: Real-World Applications: Numerous artists and designers have embraced generative AI in their creative process, resulting in remarkable artworks. Notably, collaborations between AI systems and artists have produced captivating pieces that blur the boundaries between human creativity and machine intelligence. Additionally, various tools and platforms have emerged to facilitate generative AI-based digital art creation, empowering artists with accessible and powerful tools for experimentation and expression.

A few case studies showcasing real-world applications of generative AI:
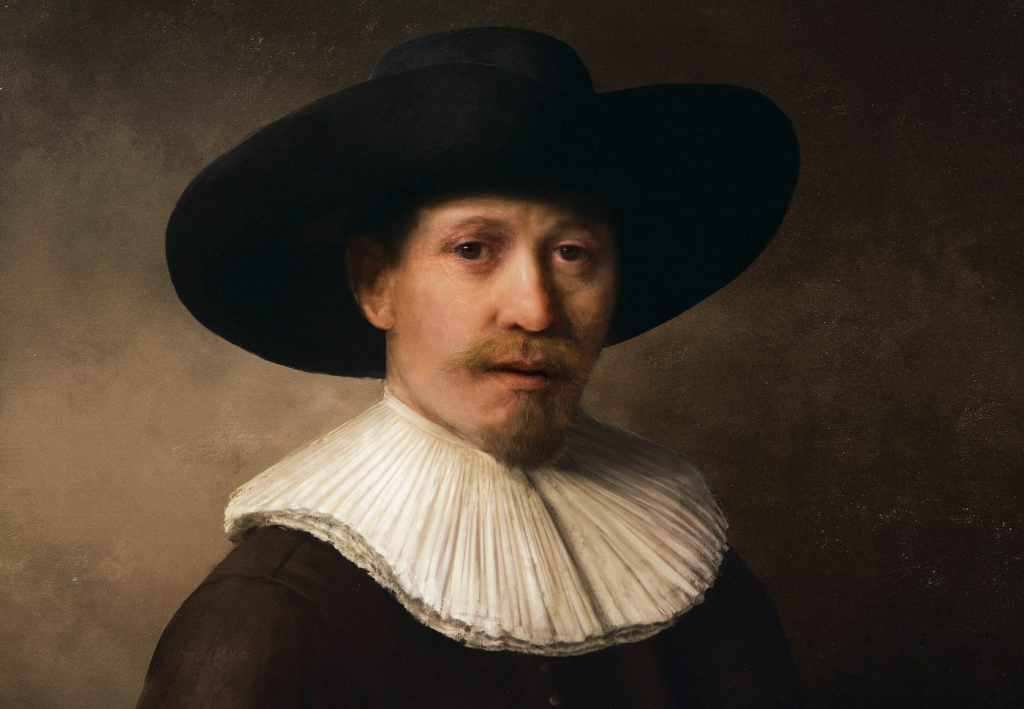

The Next Rembrandt: In collaboration with Microsoft, a team of data scientists and art historians used generative AI to create a new painting in the style of the renowned artist Rembrandt. By analyzing Rembrandt’s existing works, the AI system learned his distinctive techniques, brushstrokes, and subject matter. The resulting artwork, titled “The Next Rembrandt,” was a stunning replication that demonstrated the power of generative AI in imitating artistic styles.

DeepArt: DeepArt is an online platform that allows users to transform their photos into artworks inspired by famous artists. Leveraging generative AI algorithms, DeepArt analyzes the input image and applies the style of a chosen artist, such as Van Gogh or Picasso, to create a unique, stylized version. The platform has gained popularity, enabling users to explore different artistic styles and generate personalized digital artworks.
Magenta by Google: Magenta is an open-source project by Google, focused on exploring the intersection of AI and music. Using generative AI techniques, Magenta has developed various tools and models that can compose original pieces of music, generate melodies, and even harmonize with human musicians. The project showcases how generative AI can contribute to the creative process in music composition and expand the boundaries of musical expression.

DALL-E: DALL-E, developed by OpenAI, is a generative AI model capable of creating unique and imaginative images from textual descriptions. The model has been trained on a vast dataset of images and can generate visuals based on detailed prompts. It has the ability to conceptualize and render scenes that do not exist in the real world. DALL-E demonstrates the potential of generative AI in generating visual content based on textual input, paving the way for innovative design applications.
Prisma: Prisma is a popular mobile app that utilizes generative AI to transform ordinary photos into artworks inspired by famous artists and artistic styles. The app leverages neural networks to analyze the input image and applies a range of artistic filters, emulating the brushwork, color palettes, and textures of renowned artists. Prisma showcases how generative AI can be accessible and user-friendly, allowing individuals to experiment with various artistic styles and create visually striking images.
Advantages and Challenges of Generative AI in Digital Art and Design:
Generative AI brings several advantages to the realm of digital art. It offers artists new sources of inspiration, enables the generation of vast amounts of diverse ideas, and facilitates the exploration of uncharted territories. Moreover, generative AI can assist artists in automating certain aspects of the creative process, acting as a collaborator rather than a replacement. However, ethical considerations, potential biases in training data, and the limitations of generative models pose challenges that need to be addressed for responsible and inclusive creative practices.
Creative Inspiration: Generative AI models can serve as a valuable source of inspiration for artists and designers. By generating new and unique content, these models can spark creativity and push creative boundaries, leading to innovative and unconventional artworks.
Exploration of Uncharted Territories: Generative AI enables artists to explore unexplored territories by generating novel ideas and visual concepts. It offers the opportunity to break free from traditional artistic constraints and experiment with new styles, forms, and techniques.
Efficiency and Automation: Generative AI can automate certain aspects of the creative process, saving artists time and effort. It can assist in tasks such as generating initial sketches, suggesting color palettes, or providing variations of a design, allowing artists to focus more on the conceptualization and refining stages.
Collaborative Potential: Generative AI can act as a collaborator for artists, working hand in hand with human creativity. It can generate initial concepts or provide alternative ideas, leading to fruitful collaborations between human artists and AI systems.
Challenges of Generative AI in Digital Art and Design:
Ethical Considerations: Generative AI raises ethical concerns, especially in cases where AI-generated content is presented as the work of human artists. Proper attribution and transparency are essential to ensure ethical practices in the use of generative AI in digital art and design.
Bias and Representation: Generative AI models heavily rely on the training data they are exposed to. If the training data contains biases or lacks diversity, the generated content may reflect those biases, perpetuating stereotypes or excluding certain groups. Ensuring diverse and inclusive training datasets is crucial to avoid biases in generative AI-generated artworks.
Limitations of Current Models: While generative AI has shown remarkable capabilities, current models still have limitations. Generating high-resolution and detailed content can be challenging, and the output may sometimes lack the finesse and subtlety of human-created artworks. Continued research and advancements are necessary to overcome these limitations.
Balancing Automation and Human Creativity: While automation can be beneficial, there is a delicate balance to be struck between AI-generated content and human creativity. It is essential to preserve the unique perspectives, emotions, and experiences that human artists bring to their work, ensuring that AI serves as a tool rather than a replacement.
Future Directions and Possibilities:
Future Directions and Possibilities for Generative AI in Arts and Design:
1. Enhanced Realism and Detail: As generative AI models continue to advance, we can expect significant improvements in the realism and detail of generated artworks. Higher-resolution outputs, intricate textures, and nuanced details will enable generative AI to produce visually stunning pieces that closely resemble the quality of human-created art.
2. Interactive and Responsive Artworks: Future developments in generative AI may lead to interactive and responsive artworks. Imagine art installations that react to the presence and actions of viewers, adapting their form, color, or movement in real-time. Generative AI can enable dynamic and engaging art experiences that blur the boundaries between the artist, the artwork, and the audience.
3. Co-Creation and Collaboration: Generative AI has the potential to facilitate seamless co-creation and collaboration between human artists and AI systems. Artists can work alongside AI models, leveraging their creative suggestions, exploring alternative possibilities, and refining their artistic vision. This collaboration could result in entirely new art forms and unconventional artistic expressions.
4. AI as Artistic Toolkits: Generative AI can evolve into powerful artistic toolkits, providing artists with a range of customizable algorithms and models to experiment with. Artists can shape and train these models to suit their unique artistic styles, allowing for personalized and distinctive outputs. AI toolkits may become integral to the creative process, empowering artists with innovative tools and expanding their artistic capabilities.
5. Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Generative AI has the potential to bridge the gap between different artistic disciplines. Collaborations between artists, designers, musicians, and technologists can result in multidimensional experiences where generative AI generates visual, auditory, and interactive components. This cross-disciplinary approach can lead to immersive installations, multimedia performances, and transformative artistic experiences.
6. Generative AI as Art Critic and Curator: Generative AI can be employed to analyze and evaluate artworks, providing unique insights and perspectives. AI systems can identify patterns, styles, and themes within a vast collection of artworks, assisting curators in organizing exhibitions and helping artists gain a deeper understanding of their own work. Additionally, AI-generated critiques can offer alternative viewpoints and challenge traditional notions of artistic critique.
7. Democratization of Creativity: As generative AI becomes more accessible and user-friendly, it has the potential to democratize creativity. Artists of all backgrounds and skill levels can leverage generative AI tools and platforms to explore new artistic horizons, experiment with different styles, and create impactful artworks. This democratization can lead to a more inclusive and diverse art ecosystem.
Conclusion:
The future of generative AI in arts and design holds immense potential. Advancements in realism, interactivity, co-creation, and cross-disciplinary collaboration will reshape the creative landscape. With continued research, ethical considerations, and responsible practices, generative AI can augment human creativity, expand artistic possibilities, and inspire new forms of expression. Embracing generative AI as a tool for artistic exploration and collaboration opens doors to uncharted territories and paves the way for exciting artistic frontiers.