Digital Assurance: Protecting Your Business in a Connected World
I am sure you must have heard about “Digital Transformation” a lot everywhere. Ever wondered what actually Digital Transformation is?
Lately, the digital phenomenon stimulated the business and IT sector like never before. Unlike the Internet revolution and the DotCom madness, Digital is largely business-driven.
In this blog, I’ll cover topics like What is Digital Assurance? Why do we need it and How is Digital Assurance different from Traditional QA?
The digital transformation stampede is a combination of business transformation using IT and IT transformation using the methods of Continuous Delivery, Shift-Left, DevOps, Analytics, and Data-Driven software development. In this respect, we can say Digital represents bringing an up-to-date version of both IT and Business.
The scope of Digital spans all the new technologies including Social, Mobile, Analytics & Cloud (SMAC), BigData, Internet of Things (IoT), Drones, Artificial Intelligence(AI), and machine learning, etc.
A lot of Organisations are embarking on Digital Transformation programs that are affecting not only businesses across all industries and government sectors but also the majority of people in their daily lives.
Almost all businesses have committed to transforming themselves using technological advances – at speed – and they are calling it Digital transformation.
Digital Assurance
Digital Assurance (also called Digital Transformation Assurance) is the process of ensuring that an organization’s digital transformation efforts are successful and meet the desired outcomes.
It involves assessing the organization’s digital capabilities, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing strategies to achieve digital maturity.
Why do we need Digital Assurance?
Digital Transformation is imperative for a business’s growth and development, hence assuring the quality of Digital Transformation always plays a crucial role.
The need for Digital Assurance arises due to the following reasons:
- Complexity: Digital transformations can be complex and involve multiple departments, systems, and technologies. Digital Assurance helps organizations navigate this complexity and ensures that all components of the transformation are aligned and working together.
- Risk Management: Digital transformations often involve significant investments and carry a degree of risk. Digital Assurance helps organizations identify and mitigate these risks, protecting the organization’s investments and ensuring the success of the transformation.
- Compliance: Digital transformations can also have compliance implications, particularly in regulated industries like healthcare, insurance, banks, telecom, etc. Digital Assurance helps organizations ensure that their digital capabilities meet regulatory requirements and adhere to industry standards.
- Measuring Success: Digital Assurance helps organizations measure the success of their digital transformation efforts and identify areas for improvement. It allows organizations to assess their digital maturity, track progress, and make data-driven decisions about future investments.
- Business Continuity: Digital Assurance also ensures that the digital transformation doesn’t disrupt the existing business operations and maintains continuity.
One key aspect of digital assurance is regular testing and monitoring of software to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This can include automated testing tools, as well as manual testing performed by security experts. Additionally, incident response plans and disaster recovery plans can be an important part of digital assurance, as they help organizations respond quickly and effectively in the event of a security breach or other disruption.
Continuous Delivery explained.
Until now we have understood what is Digital Assurance and why organizations need it. Will now see how organizations acquire, build and assure their Digital systems to scale their business.
The headlong stampede to go Digital, along with the transformations required to achieve it has put more pressure than ever on IT software development professionals.
Traditionally (and for most large organizations, currently) software has been built using waterfall or structured approaches (often described as V-Model). In this approach, the target solution/ requirements are defined in great detail, and large programs of work are done to achieve the target. Almost all such projects are overrun and fail to deliver the system that meets the changing needs and requirements of the business.
The Agile approach for software development presumes that smaller, focused, motivated, autonomous teams can deliver software faster. However, large systems need a lot of architectural work making it the biggest challenge in Agile development. Integrating the diverse smaller systems later is a painful process making it another downside of Agile.
The most successful Digital transformation projects use what might be called Continuous or Adaptive approaches. These approaches, as mentioned before, use a blend of methods such as Continuous Delivery, Shift-Left, DevOps, Analytics, and Data-Driven Software development. This approach is widespread and the IT industry seems to have decided that this is the way forward with Digital.
Confused with the terminologies? What is continuous delivery, what is Shift-Left, and what not? I hear you say, No Worries!!
Let me try to break down the definition and explain in brief each term in a simple and effective manner.
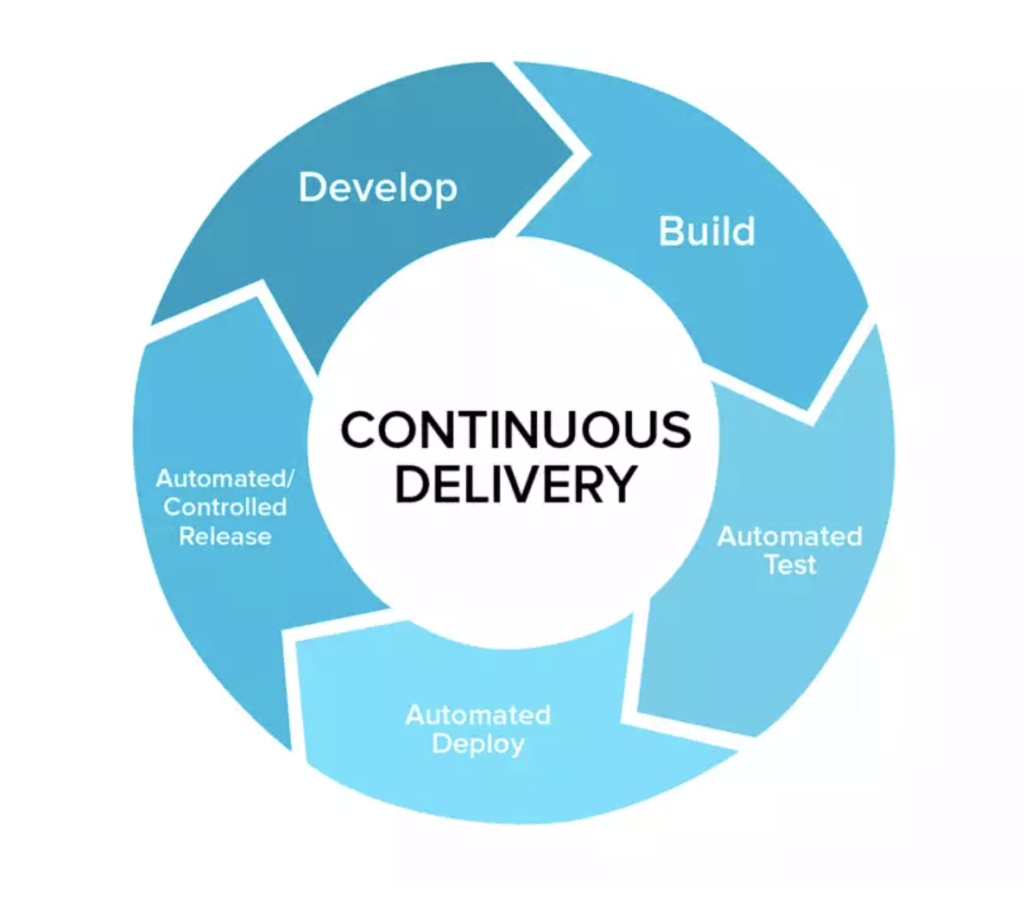
- Continuous delivery is a software development practice in which code changes are automatically built, tested, and deployed to production on a frequent, regular basis. This allows for faster delivery of new features and improvements to customers and enables organizations to respond quickly to changing business needs.
- Shift left is a software development methodology that emphasizes the importance of early testing and detection of defects in the software development process. The goal of shift left is to identify and resolve issues as early as possible in the development cycle, rather than waiting until later stages when they can be more costly and time-consuming to fix.
- DevOps is a set of practices and principles that aim to bridge the gap between software development and operations and to promote collaboration and communication between these two teams. It is based on the idea of working together throughout the entire software development life cycle, using automation, collaboration, and continuous integration and delivery practices. DevOps culture is also about empowering developers to take ownership of their code throughout the entire software development life cycle and to be able to deploy and operate their code in production.
- The role of analytics in continuous delivery is to provide insight into the performance and impact of continuous delivery processes and identify improvement areas. By tracking key performance indicators, monitoring, and troubleshooting, identifying bottlenecks, and monitoring the release process, analytics can help teams make data-driven decisions to optimize the continuous delivery process and improve the speed, quality, and reliability of software delivery.
- Data-driven software development is a methodology in which data is used to inform and guide the development process, from design to deployment. It involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to make informed decisions about the software development process, and to deliver software that meets the needs of users and the business.
How is Digital Assurance different from Traditional QA?
Digital assurance and traditional QA are both important processes for ensuring the quality and security of digital systems and processes, but they have some key differences.
Traditional testing typically focuses on ensuring that a system or application
meets specified requirements and standards, by testing its functionality,
performance, and usability.
This process is typically done during the development phase and the goal
is to identify and fix any bugs or errors before the system is deployed.
Digital assurance, on the other hand, involves assessing the effectiveness
of digital transformation projects, identifying potential risks and issues,
and making recommendations for improvement. This includes evaluating the
alignment of digital initiatives with the organization’s overall business strategy,
assessing the organization’s readiness for digital transformation, and
monitoring the progress of digital initiatives.
It also focuses on ensuring the security and compliance of a system or application.
This process is typically done after the system is deployed, and the
goal is to identify and address any vulnerabilities or risks that attackers could exploit.
Digital assurance may include activities such as penetration testing,
vulnerability assessments, and security audits, and is a continuous process
.
In conclusion, both digital assurance and traditional QA are essential for ensuring the success of digital transformation initiatives. Digital assurance provides a holistic view of the entire digital transformation process and ensures that the organization is on track to achieve its business objectives. Whereas, traditional QA ensures that the products or software developed as part of the digital transformation initiative meet the required standards.
Together, digital assurance and traditional QA provide a comprehensive approach to ensuring the quality and success of digital transformation initiatives.
Add Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.








