Snowflake Security Overview and Best Practices
In an era where data is the new gold, protecting it is no longer an option but a necessity. Snowflake ,a leading cloud data platform that revolutionizes how organizations manage and analyze data. Its architecture allows for seamless scalability, performance, and security, making it a top choice for businesses worldwide. Let’s dive deeper into Snowflake security and explore the best practices to keep your data protected.
What Makes Snowflake Secure?
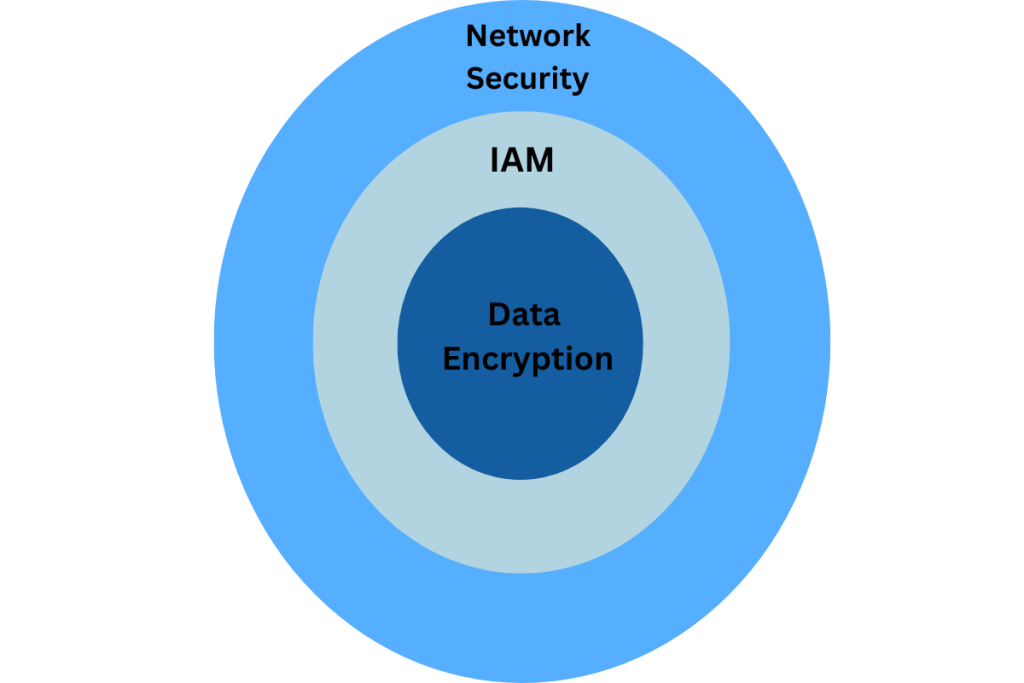
Snowflake adopts a defense-in-depth approach, leveraging three primary security layers to safeguard customer data effectively. These layers are:
Network Security
Snowflake employs robust network security measures to protect data during transmission. Encrypted connections and secure protocols ensure that data remains confidential and intact.
Identity & Access Management
IAM is crucial in controlling who can access Snowflake resources. Role-based access controls (RBAC) and granular permissions ensure that users only have access to data and functionalities essential to their roles.
Data Encryption
Snowflake prioritizes data encryption both at rest and in transit. AES-256 encryption standards are employed to encrypt data, ensuring that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable.
Best Practices for Snowflake Security
Managing Users and Roles
Effective management of users and roles is fundamental. Follow these guidelines:
- Create Role-Based Access: Assign roles based on job responsibilities to ensure users have appropriate access levels.
- Regularly Review Permissions: Conduct periodic reviews to ensure permissions align with current job roles and responsibilities.
Authentication and Single Sign-On (SSO)
Authentication is the first line of defense. Here’s how to enhance it:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of authentication significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Integrate with SSO Providers: Use trusted identity providers for seamless and secure authentication.
Sessions Management
Managing sessions effectively enhances security. Consider these tips:
- Set Session Timeout: Define session timeout periods to automatically log out inactive users, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Monitor Active Sessions: Regularly monitor and audit active sessions to detect any suspicious activities.
Object-Level Access Control (Authorization)
Controlling access at the object level is crucial. Follow these best practices:
- Use Access Control Lists (ACLs): Implement ACLs to specify who can access specific objects, ensuring data confidentiality.
- Implement Least Privilege Principle: Grant users the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks, minimizing potential security breaches.
Column-Level Access Control
Granular access control at the column level adds an extra layer of security. Consider these practices:
- Mask Sensitive Data: Use data masking techniques to hide sensitive information from unauthorized users.
- Implement Dynamic Data Masking: Dynamically mask data based on user privileges to protect sensitive data in real-time.
Row-Level Access Control
Fine-grained control over rows enhances data security. Follow these guidelines:
- Use Row-Level Security Policies: Define policies to restrict access to rows based on user attributes, ensuring data privacy.
- Implement Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Control access based on attributes such as user roles, locations, or departments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Snowflake offers robust security features backed by a defense-in-depth approach. By implementing best practices such as managing users and roles effectively, enhancing authentication with MFA and SSO, and implementing granular access controls, organizations can ensure their data remains secure and protected. Embracing Snowflake’s security features and adhering to best practices is crucial in safeguarding valuable data in today’s digital landscape.
Click here to check my previous blogs.